Floor seismic adaptation requirements
The rigidity of the base and the structural continuity are two requirements that, if met at the same time, can trigger in the building a “box action” behaviour, capable of efficiently counteracting seismic actions.
RIGIDITY OF THE BASE
In this respect, paragraph B.6 of Eurocode 8 indicates:
«Floors play an important role in the overall seismic behaviour of the structure. They behave as horizontal frameworks that not only absorb and transmit inertia to the vertical structural systems, but also ensure that these systems all contribute together to counteracting the horizontal action.
…
It is therefore of the utmost importance that floors are sufficiently rigid and strong, and that they are efficiently connected to the vertical structural elements. With this in mind, extreme attention must be paid to non-compact or extremely large configurations, or in case of large openings, particularly if these are nearby main vertical structural elements, therefore preventing and efficient connection.»
BEAM-SLAB CONNECTION
In addition to the rigidity of the base, structural continuity must also be guaranteed, through appropriate connections between the concrete slab and the beams. This connection can be obtained using the connectors listed below.
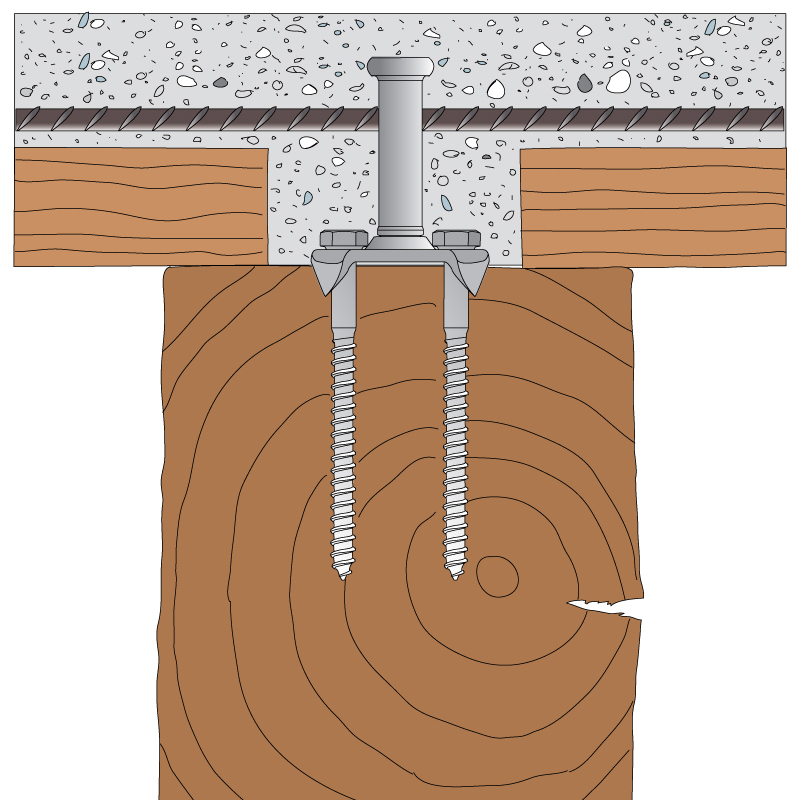
WOOD FLOOR CONNECTORS
To ensure continuity between the slab and the wood beams, use the following connectors: CTL BASE, CTL MAXI, OMEGA.
STEEL FLOOR CONNECTORS
To ensure continuity between the slab and the steel beams, use the following connectors: CTF: WELDED DIAPASON.
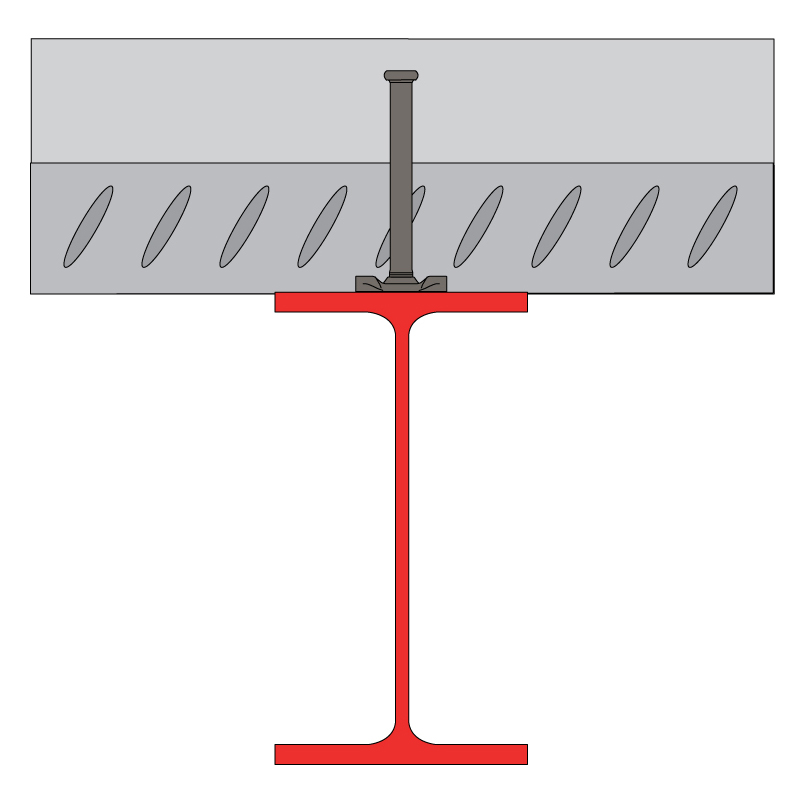
HOLLOW BRICKS AND CONCRETE FLOOR CONNECTORS
To ensure continuity between the slab and the hollow bricks and concrete beams, use the following connectors: CTCEM VCEM CTCMINI.

CONCRETE
When restoration projects are undertaken it is important to analyse the geometry and mechanical characteristics of the wood. Solid wood, glue-laminated timber can be used for new floors.
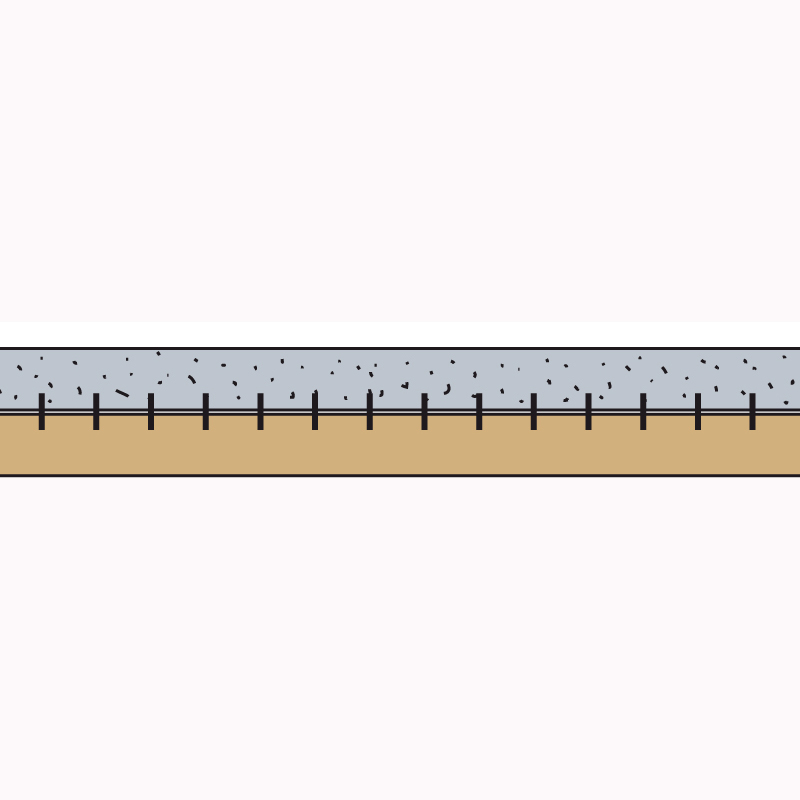
ELECTROWELDED MESH
The concrete rigid plane must always be reinforced with a suitably sized electrowelded mesh. Normally, a Ø 8 mm, mesh 20×20 cm is placed in the middle of the slab. It is not necessary to fix the mesh to the connectors.
LIGHT STRUCTURAL CONCRETES
For a reduced weight rigid plane, it is recommended to use lightweight structural concrete, which provides high mechanical resistance with a lower oscillating mass. It is especially recommended for use in seismic areas.

FIBRE REINFORCED CONCRETES
Low thickness fibre reinforced concretes (also called micro-concretes) are used more and more in the seismic improvement of buildings. Their thicknesses vary between 20 and 35 mm, and no electrowelded mesh is required. Tecnaria also produces connectors for the various types of very low thickness floors.
HOLES IN THE RIGID PLANE
Positioning the staircase hole near the edge stops the continuity of the strut or the tie rod. The diaphragm is weakened. If possible, this position must be avoided.
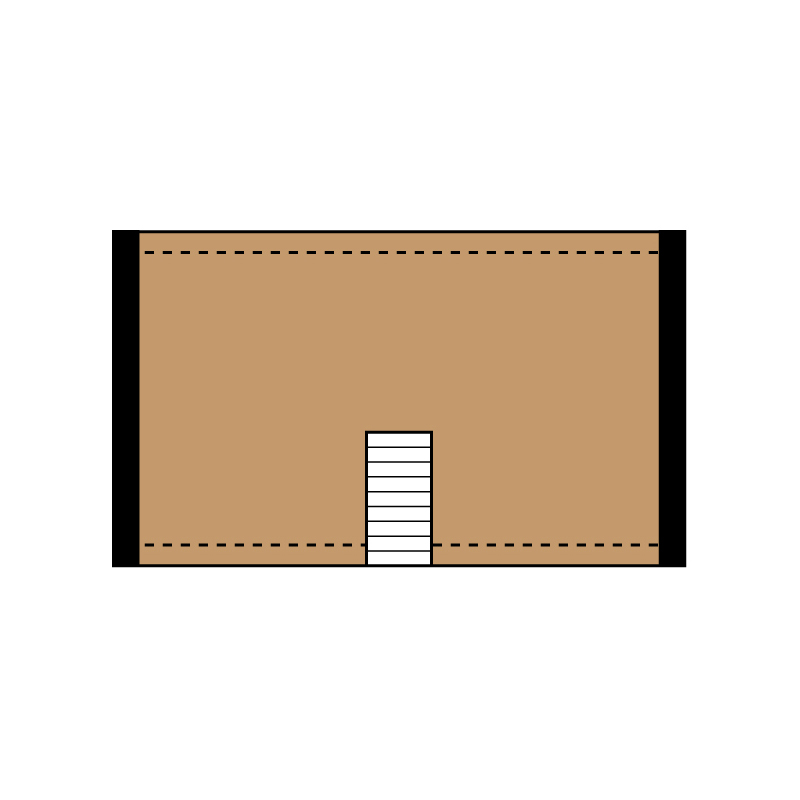
HOLES IN THE RIGID PLANE
The hole in this position does not stop the strut of the diaphragm. Preferred position.
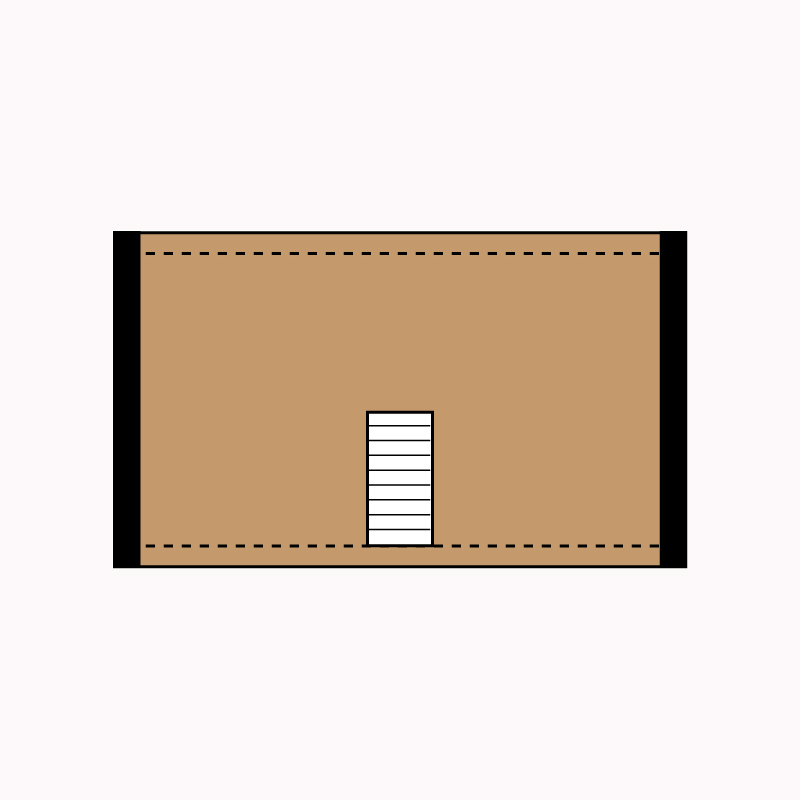
HOLES IN THE RIGID PLANE
A staircase hole in this position does not allow good connection to the wall, or a good performance of the diaphragm. If possible, this position must be avoided.
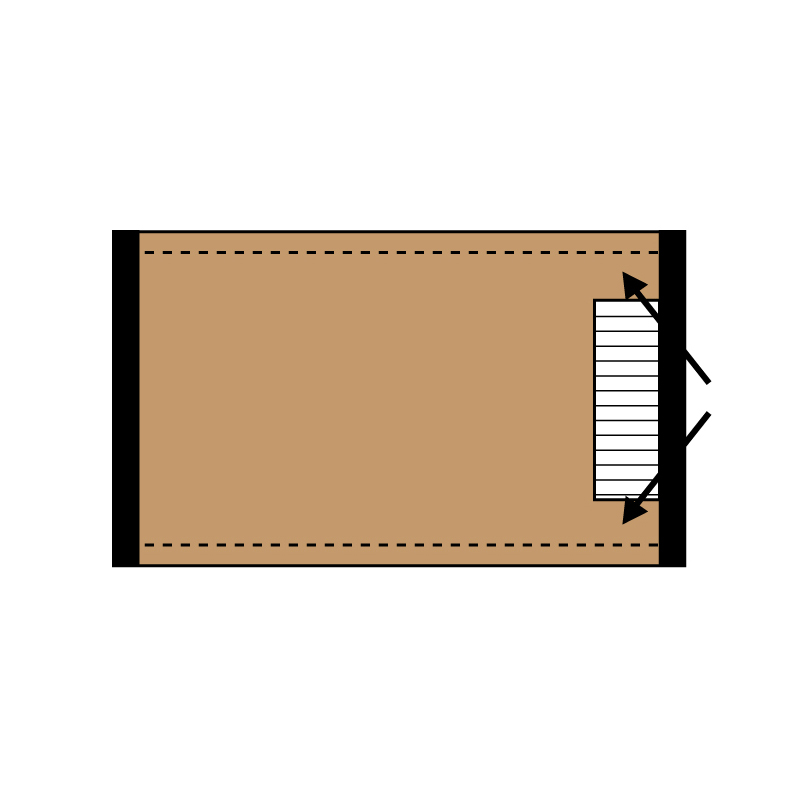
HOLES IN THE RIGID PLANE
The hole in this position does not interrupt the strut or the tie rod, and does not impair the connection to the walls. Optimum position.

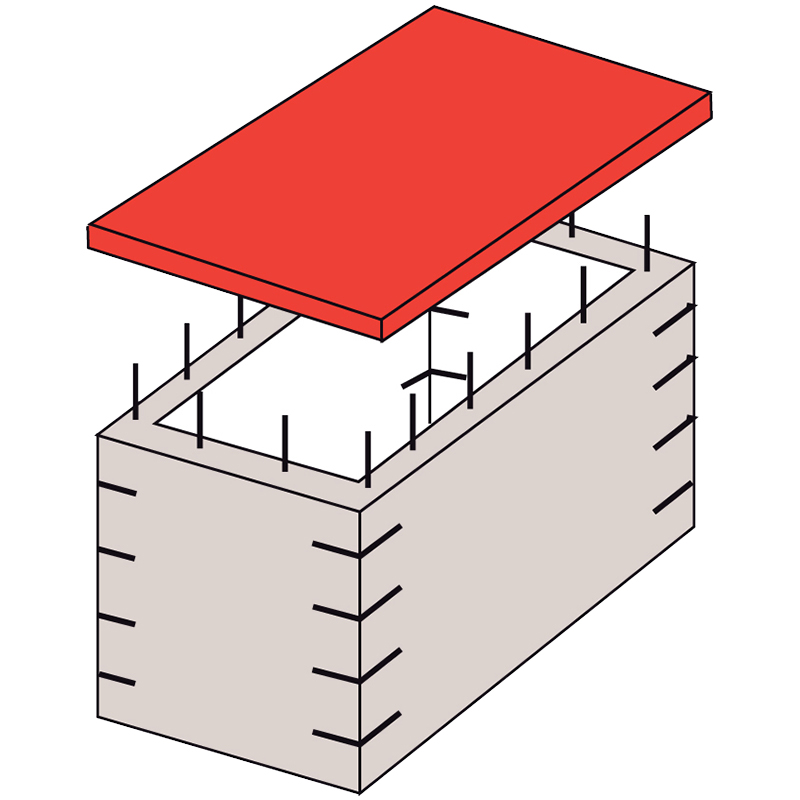
STRUCTURAL CONTINUITY

BOX ACTION
Structural continuity must also be guaranteed, through appropriate connections between the floor, the masonry and the cover in addition to the rigidity of the base.
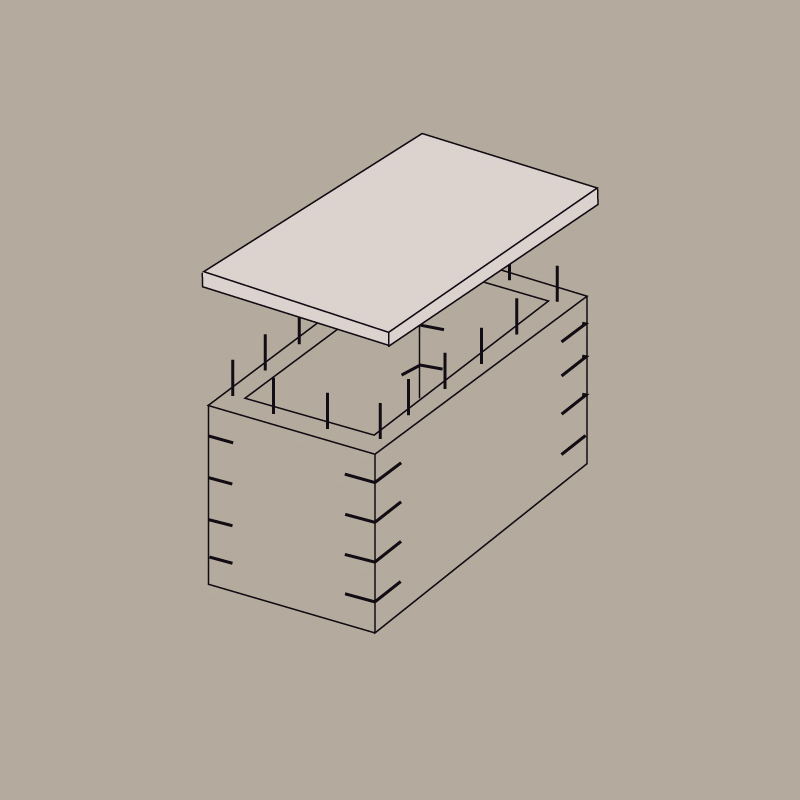
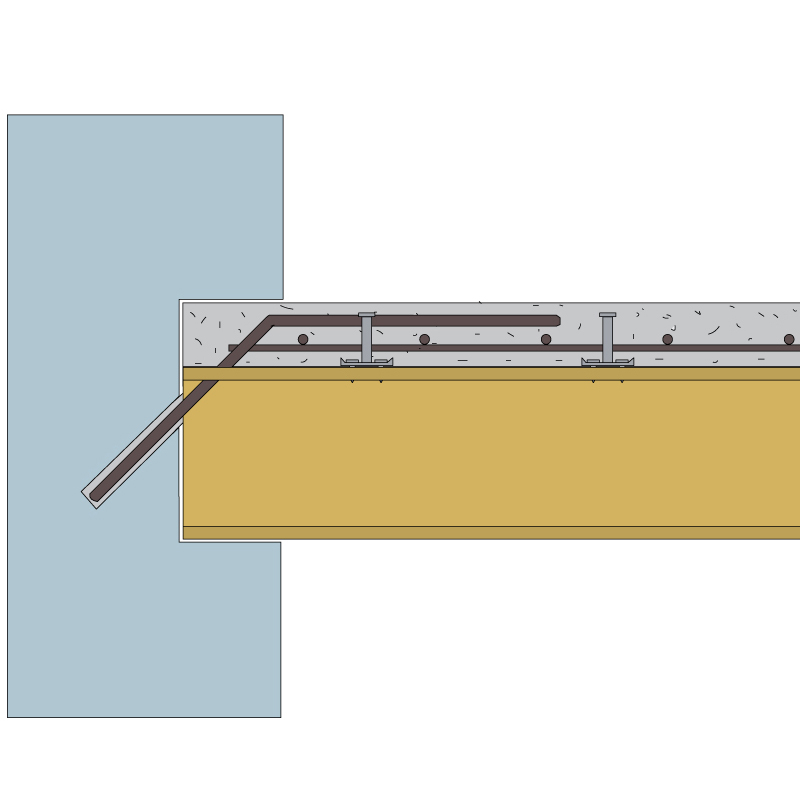
CONNECTION TO THE MASONRY – PERIMETER BEAMS
Perimeter beams are an integral part of the structure in new buildings and guarantee the box action. This connection with the slab has advantages in terms of stiffness and seismic resistance of the floor.
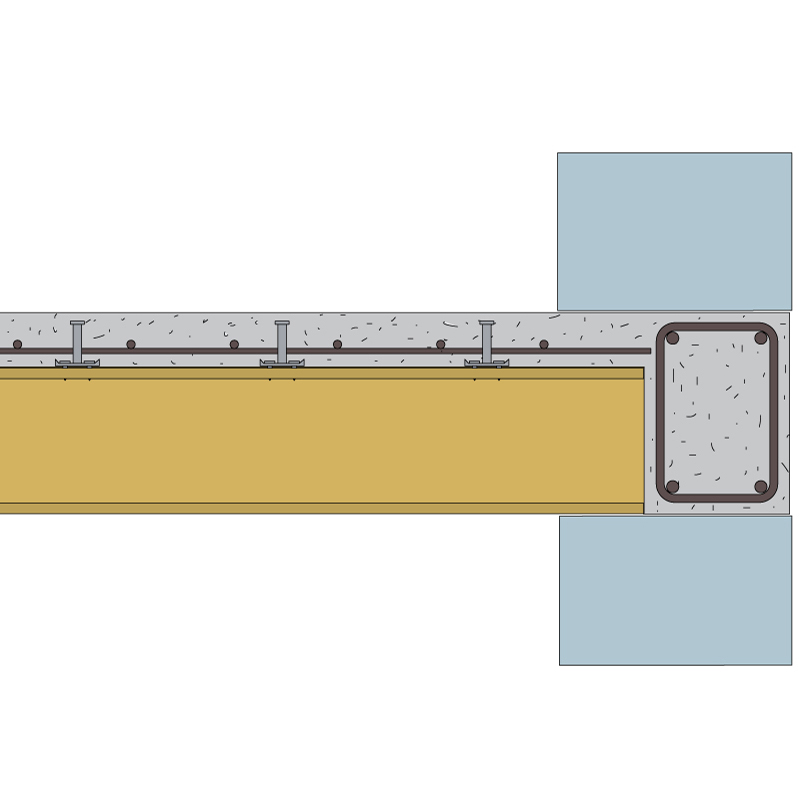
ANTI-SEISMIC CONNECTION TO THE WALLS – BARS AND RESIN
If the existing floor does not have perimeter beams resting on the walls, it is recommended that the slab be joined to the bearing walls around the perimeter of the floor, to ensure the box action of the building. This precaution brings benefits in terms of stiffness and seismic resistance of the floor. In general, this entails the installation of rebars, embedded in Tecnaria RTEC 400 epoxy resin.